Varicose Veins
What are varicose veins?
Varicose veins occur when veins in the legs become enlarged, dilated, and overfilled with blood. Varicose veins typically appear swollen and raised, and have a bluish-purple color.
Normal venous flow dynamics and what happens in varicose veins ?
In most cases, varicose veins appear on the lower legs. That's because standing and walking upright increases the pressure in the veins of leg. To push blood back to your heart, veins rely mainly on surrounding muscles and a network of one-way valves. As blood flows through a vein, the cup-like valves alternately open to allow blood through, than close to prevent backflow.
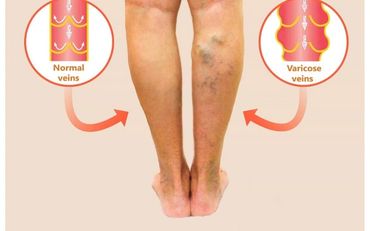
In varicose veins, the valves do not work properly -- allowing reflux of blood in the vein. Instead of flowing from one valve to the next, the blood continues to pool in the vein, increasing venous pressure and congestion causing the vein to bulge and twist. Because superficial veins have less muscle support than deep veins, they are more likely to become varicose.
Potential factors leading to varicose veins:
- Occupation associated with prolonged standing: teacher, police, bus conductor, vegetable vendors, barber, sales man, factory workers
- Older age
- Female sex
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Genetics also plays a role, so if other family members have varicose veins there is a greater chance you will, too
Symptoms of varicose veins:
- Bulging veins: Twisted, swollen, rope-like veins are often blue or purple in color. They appear just below the surface of the skin on the legs, ankles and feet.
- Heavy/aching or tender legs: Muscles in the legs may feel tired, heavy or sluggish, especially after prolonged standing and gets partially relieved by leg elevation.
- Itching: The area around the varicose veins may itch.
- Swelling: around the leg and ankle.
- Skin discolorations: If left untreated, varicose veins can cause brown/bluish discolorations on the skin.
- Venous ulcers (sores) on the skin can result from severe varicose veins. Mostly they occur in lower leg and around ankle.
- Bleeding. Occasionally, veins very close to the skin may burst. This usually causes only minor bleeding. But any bleeding requires medical attention.
- Sometimes varicose veins clot and become painful, tender, hard and discoloured. This is called phlebitis, a painful but temporary condition.
5 Stages of venous disease
- Stage 1: Spider veins or reticular veins: tiny threads like veins in a spider-web or cluster-like pattern. Usually asymptomatic and are associated with family history, menopause and hormonal imbalance.
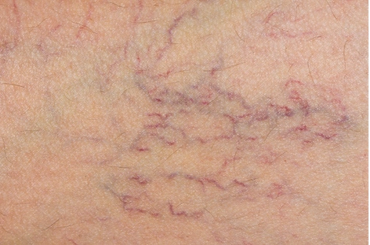
- Stage 2: varicose veins
- Stage 3: swelling in leg and ankle
- Stage 4: skin discoloration, itching, skin thickening and hardening (Lipodermatosclerosis)
- Stage 5: Ullcer and open sores
Diagnosis of varicose veins
Doppler Ultrasonography: Type of vascular ultrasound to assess blood flow and structure of leg veins.
Treatment of Varicose Veins
Specific treatment is determined by the doctor based on
- Age, overall health, and medical history
- Extent of the condition
- Signs and symptoms
- Expectations for the course of the condition
Treatment may include
- Elevation of the legs. To elevate your feet above the level of your heart 3 or 4 times a day for about 15 minutes at a time..
- Compression stockings. These elastic stockings squeeze the veins and prevent blood from pooling. Compression stockings are effective only if they are worn every day.
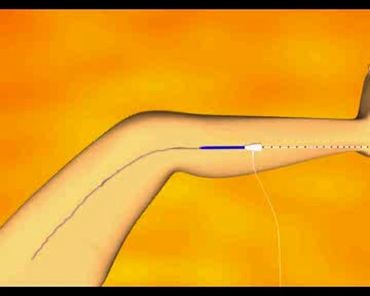
- Radiofrequency (RFA)ablation or Laser ablation:
- Is currently considered the gold standard treatment for varicose veins. The procedure is done under ultrasonography (USG) guidance.
- Through a 3mm incision, a tiny fiber is inserted into from a lower leg superficial vein and navigated up to the vein in groin. The laser or radio frequency energy is used to deliver heat that destroys the wall of the varicose vein and then closes the abnormal vein.
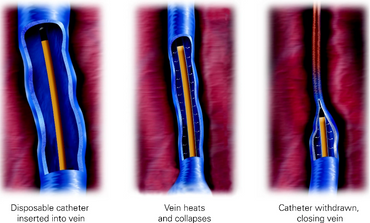
- It is simple, risk-free and quick procedure allows the patients to return to normal life sooner and in much better health. The procedure is done with single needle puncture leaving no scar.
- Chances of recurrence are minimal. The small residual or recurrent varicosities can be treated on OPD basis with just simple injections called as sclerotherapy. Recurrences are more common in young age and in patients with strong family history.
Before and After Treatment
How does the leg drain blood out after treatment of varicose veins?
The leg has two systems of veins, the deep and the superficial. Between these two systems there are many collateral pathways to enable normal venous blood flow. When the diseased superficial system is treated, the blood gets redirected into the deep system without affecting blood flow in the leg.
Post procedure course
- Can walk after anaesthesia effect weans off.
- Avoid prolonged standing for next 3-5 days.
- To wear graduated pressure venous stockings to support the legs.
- Few patients may have short lasting tenderness along the course of the vein.
- Few patients may have numbness in lower leg and ankle region which may resolve in a month to 3 months.
Varicose Veins
If you are suffering from Varicose Veins, you would have searched on Varicose Veins treatment methods. This video highlights the differences and similarities between Endovenous Laser and Glue treatment.

