આર્ટરીયોવીનસ માર્લ્ફોમેશન (એ.વી.એમ.– બઓ)
આર્ટરીયોવીનસ માર્લ્ફોમેશન (એ.વી.એમ. – બઓ) એટલે શું ?
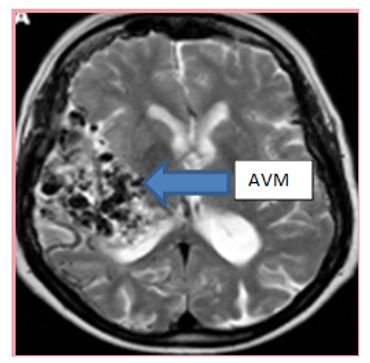
સ્ટ્રોક એ.વી.એમ. એટલે ધમણી અને શીરા વચ્ચેના અસામાન્ય જોડાણથી બનતો રુધિર કેશીકાઓ નો ગુચ્છો. એ.વી.એમ. શરીરના જુદા જુદા અવયવોમાં થઈ શકે છે. પરંતુ મગજમાં થતા એ.વી.એમ. સૌથી વધુ તકલીફ દાયક રહે છે.
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
WHAT IS AN AVM?
An arteriovenous malformation, or AVM is an abnormal tuft of vessels between arteries and veins without intervening capillary network. AVMs can occur in different organs of the body, but brain AVMs are the most problematic.

એ.વી.એમ. ૮બઓ૯ ના લક્ષણો શું છે ?
લગભગ અડધા દર્દીઓને મગજનું હેમરેજ થયા બાદ જ ખબર પડે છે કે તેમને એ.વી.એમ. છે. અન્ય અડધા દર્દીઓ માથાનો દુખાવો, પક્ષઘાતના હુમલા વગેરે લક્ષણોથી પ્રભાવિત હોય છે.
એ.વી.એમ. ૮બઓ૯ ના કિસ્સાઓમાં હેમરેજ થવાની શકયતા કેટલી રહે છે ?
મગજના એ.વી.એમ. લગભગ ૦.૧ ટકા વસ્તીને અસર કરે છે. ચોક્કસ કારણ જાણી શકાયું નથી અને ગર્ભાશયમાં રકતવાહિનીઓના અસામાન્ય વિકાસને કારણે હોવાનું માનવામાં આવે છે. મુખ્યત્વે તે જન્મથી જ હાજર હોઈ શકે. જેમ જેમ વર્ષો વીતતા જાય છે, તેમ તેમ તે મોટુ થતું જાય છે. ઘણી વખત ધમણીમાં થતું લોહીનું દબાણ શીરા (વેઈન) નિયંત્રણ કરી શકતા નથી. આવા ખોડખાપણ વાળા માર્લ્ફોમેશનમાં ૧૦ થી પપ વર્ષની વય વચ્ચે રકતસ્ત્રાવ થવાની શકયતા રહે છે. પપ વર્ષ પહેલા રકતસ્ત્રાવની શકયતા દર વર્ષ ૩ થી ૪ ટકાની વચ્ચે હોય છે. (આશરે ૧ ટકા મૃત્યુની ઘટના સાથે) એક વખત એ.વી.એમ. ના દર્દીને રકતસ્ત્રાવ થઈ જાય, પછી બીજા વર્ષનું જોખમ પ્રથમ વર્ષના પ્રમાણમાં ર૦ ટકા સુધી પહોંચી શકે છે અને આગામી કેટલાક વર્ષોમાં ધીમે ધીમે ઘટીને પાછું ૩ થી ૪ ટકા સુધી આવી જાય છે.
એ.વી.એમ.ના નિદાન માટે કયું પરિક્ષણ થઈ શકે ?
મગજના એમ.આર.આઈ. એક આદર્શ તપાસ પધ્ધતિ છે. જોકે ડીજીટલ સબસ્ટ્રેકશન એન્જીયોગ્રાફી ૮મકબ૯ એ.વી.એમ. ના નિદાન માટે ગોલ્ડ સ્ટાન્ડર્ડ અને ફરજીયાત રહે છે. જયારે રકતસ્ત્રાવ (હેમરેજ) થતો હોય તેવા કિસ્સાઓમાં એ.વી.એમ. કેટલીકવાર ઈન્ટ્રા સેરીબ્રલ રકતસ્ત્રાવ ૮યહજ૯ દ્વારા સંપૂર્ણપણે અસ્પષ્ટ થઈ જતું હોય છે તેવા સંજોગોમાં ડીજીટલ સબસ્ટ્રેકશન એન્જીયોગ્રાફી ૮મકબ૯ ખુબજ કામમાં આવે છે.
What Are The Symptoms Of AVM?
About half of the patients find out they have an AVM only after they suffer a brain haemorrhage. The other half are affected by, headaches, seizures and stroke symptoms.
What are the chances of haemorrhage in an AVM?
Brain AVMs affect about 0.1% of the population. Exact cause is not known and is thought to be due to abnormal development of blood vessels in utero and may be present since birth. As the years go by, it tends to enlarge as the great pressure of the arterial vessels cannot be handled by the veins that drain it. These malformations are most likely to bleed between the ages of 10 — 55. Before 55, the likelihood of haemorrhage is between 3 and 4% per year (with a death incidence of about 1%). Once an AVM patient has bled, the risk of having another one might approach 20% during the first year, and gradually lessen to about 3 — 4% over the next few years.
Diagnostic test?
MRI brain is an ideal screening modality. However AVMs can be missed on non-invasive imaging and for final diagnosis and for evaluation before treatment Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is mandatory. In cases when bleeding has occurred, the AVM can sometimes be completely obscured by intracerebral bleeding.
એ.વી.એમ.ની સારવાર કેવી રીતે થઈ શકે ?
સારવારની મુખ્ય ચાર રીતો છે. એન્ડોવાસ્કયુલર એમ્બોલાઈઝેશન (તકલીફ દાયક ધમણીને બંધ કરી દેવી), માઈક્રો ન્યૂરોસર્જીકલ એકસીસન (ન્યૂરો સર્જરી વડે તકલીફ દાયક ગુચ્છાની કાપકુપ કરી કાઢી નાખવું), રેડિયો સર્જરી (રેડિયેશન દ્વારા એ.વી.એમ. ને કાપી અને બાળી નાખવું) અને દવાઓથી સારવાર. આ ચારેય પધ્ધતિઓ પોતાની રીતે અલગ અલગ અથવા એક બીજા સાથે સંયોજનમાં આપવામાં આવે છે.
૧. એન્ડોવાસ્કયુલર એમ્બોલાઈઝેશન
આ પ્રક્રિયામાં કોઈપણ જાતની કાપકુપ કરવામાં આવતી નથી. એક ખુબજ પાતળી નળી પગની ધમણીમાંથી નાખીને એ.વી.એમ. ૮બઓ૯ સુધી પહોંચાડવામાં આવે છે. એમ્બોલીક એજન્ટ (ઓનિકસ / મેડિકલ ગુંદર) એ.વી.એમ. ના ગુચ્છામાં ઈન્જેકટ કરવામાં આવે છે. એ.વી.એમ. ના કદ ના આધારે એક અથવા ઘણી બધી જગ્યાઓએ આ અમ્બોલીક એજન્ટ (મેડિકલ ગુંદર) ઈન્જેકટ કરવું પડતું હોય છે. આ પ્રક્રિયાને રેડિયેશન અથવા સર્જરી જેવી અન્ય સારવાર સાથે પણ કરી શકાય છે.
How Is It Treated?
There are 4 main modes of treatment. Endovascular embolization, Micro neurosurgical excision, Radio-surgery and Expectant (medical),. These are given alone or in combination based on the clinical and radiological data. It is determined by the size of your AVM and also the location. Combination therapy may also be used.
1. Endovascular Embolization
A small catheter (hollow tube) is advanced from the leg artery, into the brain vessels supplying the AVM. A non-adhesive liquid embolic agent(onyx) or glue is injected into the AVM nidus. Depending on the size of AVM it can be done in single or multiple sessions. It may be combined with the other treatments such as radiation or surgery.

ર. માઈક્રો ન્યૂરોસર્જીકલ એકસીસન (ન્યૂરો સર્જરી વડે તકલીફ દાયક ગુચ્છાની કાપકુપ કરી કાઢી નાખવું)
એ.વી.એમ.ની સારવાર માટે આ સૌથી જુની પધ્ધતિ છે. એ.વી.એમ. માટે શસ્ત્રક્રિયાના જોખમો વધારે હોય છે. કારણ કે આવા એ.વી.એમ. મગજના ખૂબજ મહત્વપૂર્ણ ભાગોમાં જોવા મળતા હોય છે તેથી શસ્ત્રક્રિયા દરમિયાન સામાન્ય રીતે નોર્મલ મગજના તંતુઓને ઈજા પહોંચવાની તથા રકતસ્ત્રાવ થવાની તથા મગજના જરૂરી ભાગોને રકત ન મળવાની તકલીફ થઈ શકે છે.
૩. સ્ટીરીયોટેકટીક રેડિયો થેરાપી (રેડિયેશન દ્વારા એ.વી.એમ. ને કાપી અને બાળી નાખવું)
આ પ્રક્રિયામાં એક પાતળી એકસ–રે બીમ એ.વી.એમ. પર કેન્દ્રિત કરવામાં આવે છે અને એ.વી.એમ. માં ઉચ્ચ ડોઝના એકસરે થી લેસર ટ્રીટમેન્ટ કરવામાં આવે છે. આ કિરણોથી ૮૦ ટકા દર્દીઓને ૩ વર્ષના સમયગાળામાં બંધ કરી શકાય છે. જયાં સુધી એ.વી.એમ. સંપૂર્ણ પણે બંધ ન થાય ત્યાં સુધી રકતસ્ત્રાવનું જોખમ યથાવત રહે છે. આ સારવાર માત્ર નાના કદના એ.વી.એમ. માં જ કરી શકાય છે. મગજના જરૂરી હિસ્સા તથા અંદર આવેલા એ.વી.એમ. માં આ સારવાર કામમાં આવે છે.
4. મેડિકલ મેનેજમેન્ટ
એવા દર્દીઓ જેમાં એ.વી.એમ. માંથી રકતસ્ત્રાવ ન થયો હોય અથવા મોટા કદના એ.વી.એમ. જેની સલામત રીતે સારવાર કરી શકાતી નથી તેવા સંજોગોમાં મેડિકલ મેનેજમેન્ટ કરવાની જરૂરીયાત રહે છે. રકતસ્ત્રાવના જોખમ ને કારણે અપેક્ષિત સારવાર પસંદ કરી શકાય છે.
2. Stereotactic Radiotherapy
A narrow x-ray beam is focused on the AVM such that a high dose is concentrated on the AVM. This radiation causes the AVM to close off over a period of 3 years in up to 80% of patients. Until the AVM is completely closed off, the risk of bleeding still persists. This treatment can only be performed in small size AVM and is preferred in deep seated location.
3. Micro neurosurgical excision
This is the oldest method for treating AVMs. The risks of surgery are considered to be high for AVMs that are located in deep parts of the brain with very important functions. So surgery is usually indicated in those patient who are bled with large hematoma or the AVM is superficial and in non eloquent part of the brain.
4. Medical (Expectant) management
In patient with unruptured AVM or large AVMs which cannot be safely treated, expected management can be opted with due risk of bleeding.

